1.What is an airlock rotary valve
Airlock rotary valves are used at solids handling processes interfaces, typically when it is necessary to separate 2 areas under different conditions (pressure most of the time) while letting the solid go from one condition to another.
Rotary valves, also commonly called star valves, are therefore used at the beginning and at the end of pneumatic transports. They allow to bring the solid from a zone of low pressure to a zone of low pressure at the beginning of the line while helping to disengage the solid from the air flow a the end of the line.
Such valves are able to perform a rough dosing, thus, they can also be installed as dosing equipment, although it is not a good practice.
2 types of airlock rotary valves are available : a drop through type and a blow through type. Both types are basically giving the same results, however, the way they do it and their characteristics are slightly different.
Airlock feeders are used widely in the industry with applications in the following areas :
- Food industries (baking, dairy, coffee, grains)
- Construction (cements, asphalt)
- Pharmaceuticals
- Mining
- Energy (power plants)
- Chemicals / Petrochemicals / Polymers
Rotary feeders working principles and main specifications are given below.
2. Drop Through rotary valve and Blow Through rotary valve
Drop Through airlock rotary valve

Drop through airlock rotary valves are “dropping” the product to the pipe or equipment below. There is an entry flange and an outlet flange.
Blow through airlock rotary valve

Blow through star valves are directly connected to a conveying line. The air used in the conveying line is therefore directly going through the alveoles of the valves, sweeping the product away
Typically, blow through valves are used either when there is a very limited height or when the product has a tendency to stick inside the rotor. For other applications, the drop through model is quite preferred.
Having the rotor directly in the pipe flow can lead to larger breakage of the product being transported, it is especially the case if several drop through valves are in series in a same piping. For this particular case, drop-through valves may be considered in order to preserve the product.
3. Star Valve Clearance and Contact detection
Star valves have typically very small clearance in between the rotor blades and the stator, it is necessary in order to provide an air sealing in between upstream and downstream areas that are not at the same pressure.
Typical clearance for airlock rotary valves is 0.1 mm and usually ranges from 0.05mm to 0.25 mm depending on the service expected for the valve (high difference of pressure from each side of the valve or not). This is a very small clearance which explains that rotary valves often suffer of scratches due to contact rotor / stator. The following table is summarizing common causes of contacts.
4. Explosion protection
A rotary airlock can be used as an isolation elements to prevent dust explosion to propagate in an installation. For this, the airlock rotary valve must be certified to be explosion shock resistant and flame proof.
In order to get those characteristics, the valve must be designed so that :
- The body and rotor can withstand the pressure of an explosion – typically 10 bar g
- The clearance tip of the blades / housing must be less than 0.2 mm
- At least 2 blades in each side of the valve must be in contact with the housing (which means that the total number of blades must be > or equal to 8
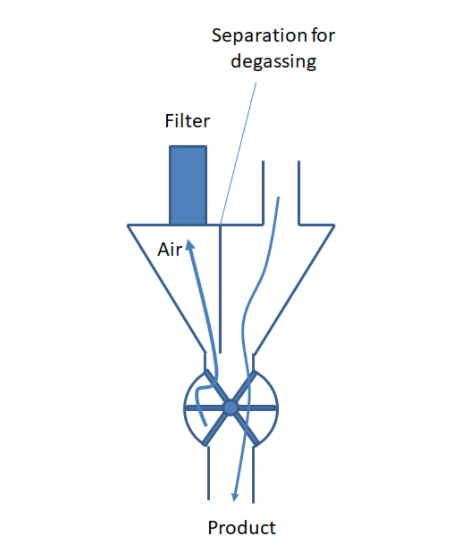
5. Rotary Valve Degassing
A low clearance will allow a good sealing and reduce the rotary airlock valve leakage. However even reduced a leakage will happen. As well, the air trapped in each pocket will also be released when the pocket is opened to the low pressure area. This leads to leakage of air.
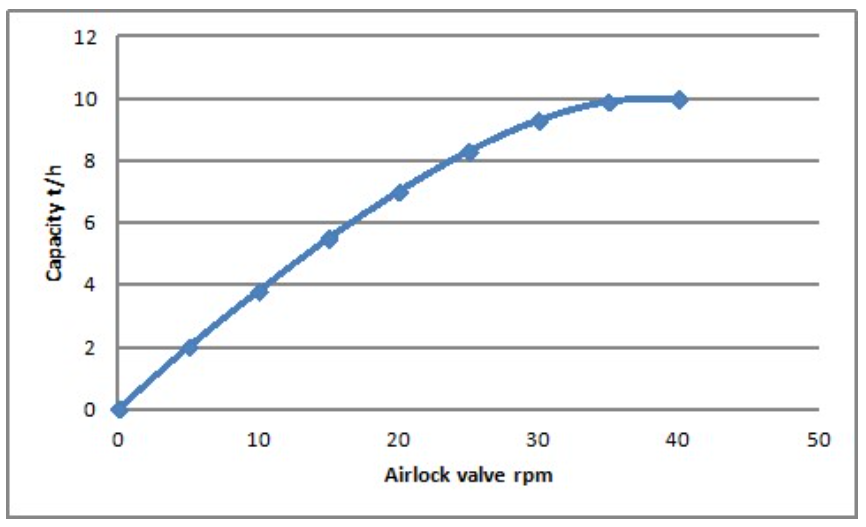
The air leakage is increasing with the difference of pressure and increases with the rotation speed of the valve. It can be very detrimental to the performance of the valve, especially with light powder, since the air released will actually fluidize the powder and prevent it to fill the pocket.
This phenomena can be witnessed in the performance curves of airlock rotary blades : the capacity will reach an assymptot and even decrease at high speed since the pockets cannot be filled anymore by the product, too much fluidized to have time to fall in the pockets.
To control this phenomena and improve the performances of the valve, a proper venting of the rotary valve must be implemented. A degassing channel is mounted on the side the pockets are returning up in order to empty them from the air prior they pick up new product. The channel is sending the air to a filter to be released.
6. Airlock rotary valve design calculations (sizing)
The capacity calculation of a star valve to achieve a given throughput is a function of the star valve diameter, its target rotation speed and the nature of the product,
- The bigger the star valve, the higher will be the capacity.
- A higher rotation speed generally means more throughput but the throughput will cease to increase past a certain speed
- The more fluid is the powder, the higher will be the throughput, there again too light products will create a limitation in throughput at a certain rotation speed Throughput can be estimated from supplier’s abascus, but the knowledge of the product will be a key input.
7. Common problems with airlock rotary valves
Different problems can affect a star valve during its operation. Common problems are among the following :
- Performance below design (lower throughput than expected)
- Damage by metal / metal contact
- Wear
8. Airlock rotary valve buying guide – How to select an airlock rotary valve
Airlock rotary valve for sale : Buying a new airlock rotary valve
When sourcing a new airlock rotary valve for your factory, the following questions need to be asked in order to buy the right specifications :
●Is the airlock rotary valve design better as blow through or drop through ?
●Do you need a special material (for instance stainless steel) or standard execution is sufficient ?
●What is the throughput you need and what is the bulk density of the material to process, it will give the diameter of the valve
●Is the valve submitted to heat ? Does it need to have specific rotor stator clearance ?
●Is the valve feeding to a pressure pneumatic conveying line ? Does it need degassing ?
●Is there a need of frequent access for cleaning inside the valve ?
●Is the powder free flowing or specific blades and pocket design is required ?
●Does the airlock rotary valve need to be certified for processing in a dust explosion area ? If yes, which zone classification is to be considered in and around the valve ?
●Does the valve need to be resistant to explosion (typically 10 bar) ?
If you have demand for rotary airlock valves and diverter valves in the pneumatic conveying lines, please feel free to contact us.
Post time: Aug-14-2021
